Instrumented Indentation and Force-Displacement Curve.
The instrumented indentation test, also known as nanoindentation, provides more comprehensive information than just a hardness value. More specifically, a force-displacement curve is recorded while a tip penetrates the measured surface. The result represents the eslastic-plastic deformability of a material.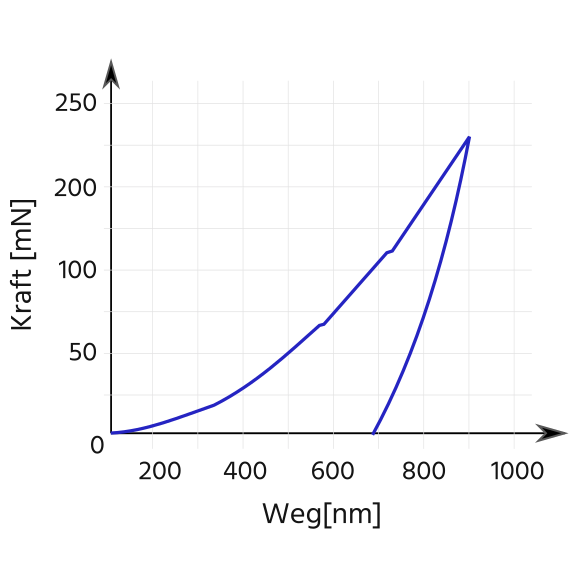
Force-displacement curve - more than just a hardness value
The force-displacement curve allows the mechanical characterization of elastic and plastic properties. Among other things, the elastic indentation modulus (EIT) is calculated. Further characteristic values are:Conclusions towards the strength can also be drawn. During the measurements, it is particularly important to ensure a vibration-free test environment and an appropriately smooth specimen surface, because these factors have a considerable influence on the accuracy.
The typical fields of application for instrumented indentation testing are found in the areas of damage analysis, coating testing, ambulatory applications (including pipeline testing) and in the testing of miniaturized components. Instrumented indentation testing is standardized according to ISO 14577.Order measurements:
#12 Material Testing
Instrumented Indentation
Instrumented indentation testing is a method used to analyze the mechanical properties of materials, particularly in materials research and testing. This testing technique allows for precise evaluation of the force-displacement curve and is used to characterize hardness, elastic properties, as well as derive insights into material strengths.